Today, let’s explore why the Internet of Things (IoT) is experiencing a surge in awareness and adoption in recent years. The diagram provides five apparent factors driving this growth, so let’s walk through each step.
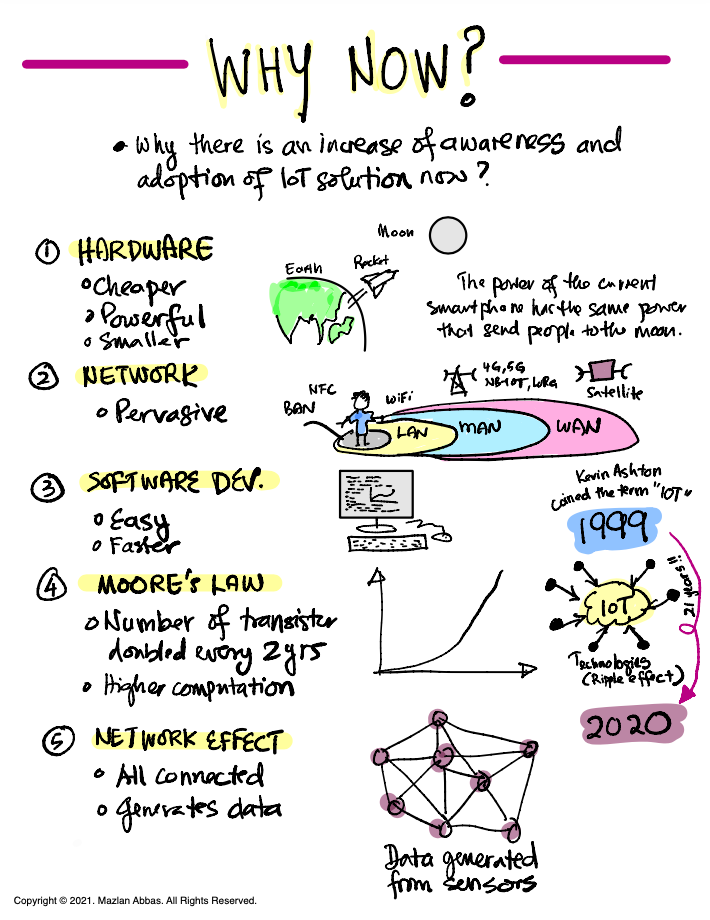
1. Hardware Advancements
The first driver of IoT adoption is the rapid development of hardware. Devices are now:
- Cheaper: The cost of sensors, processors, and connectivity modules has dropped significantly.
- More Powerful: Today’s smartphones, for instance, are as powerful as the computers that send astronauts to the moon.
- Smaller: Miniaturisation has made it easier to embed technology into all sorts of devices, from wearable health trackers to smart home appliances.
These advancements make IoT devices accessible to more people and industries.
2. Network Expansion
IoT depends on connectivity, and networks have become more pervasive and diverse:
- We now have Wi-Fi, 4G/5G, LoRa, NFC, and even satellite networks connecting devices across the globe.
- This widespread coverage ensures that IoT devices can communicate, no matter where they are located.
Imagine this: You can monitor a sensor in a remote farm or track a shipping container in the middle of the ocean because of this pervasive network infrastructure.
3. Easier and Faster Software Development
Creating IoT solutions has become simpler because:
- Software tools and platforms are now more user-friendly.
- Developers can build and deploy solutions quickly with pre-built frameworks, cloud computing, and open-source libraries.
What used to take months or years to program can now be done in days or weeks, speeding up innovation in IoT.
4. Moore’s Law: The Power of Computation
You may have heard of Moore’s Law, which states that the number of transistors on a chip doubles approximately every two years. This leads to:
- Higher computational power: Devices can handle more complex tasks, such as AI and data processing, on smaller chips.
- Lower costs over time: IoT solutions can scale quickly with more powerful chips becoming affordable.
This exponential growth in computing power has made IoT a reality.
5. The Network Effect
The network effect explains how IoT becomes more valuable as more connected devices. Here’s why:
- Everything is connected: Sensors, devices, and systems communicate and generate data.
- Data generation: The more devices there are, the more data we have. This data can be analysed to gain insights, optimise processes, and improve decision-making.
For example, a smart city network with connected traffic lights, sensors, and cameras can reduce congestion and improve safety by analysing real-time data.
Historical Context
- The term “IoT” was first coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999.
- It took years of technological progress for IoT to become mainstream. By 2020, IoT reached a tipping point, integrating with industries worldwide.
Why Now?
The convergence of cheaper hardware, pervasive networks, faster software development, computational power (thanks to Moore’s Law), and the network effect have created the perfect environment for IoT to flourish.
IoT is no longer a futuristic concept — it’s a reality shaping industries like agriculture, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Let’s discuss: Which of these factors do you think has had the biggest impact on IoT adoption? How can we use these advancements to innovate further in our fields?
[Note: Download full IoT Notes eBook]
