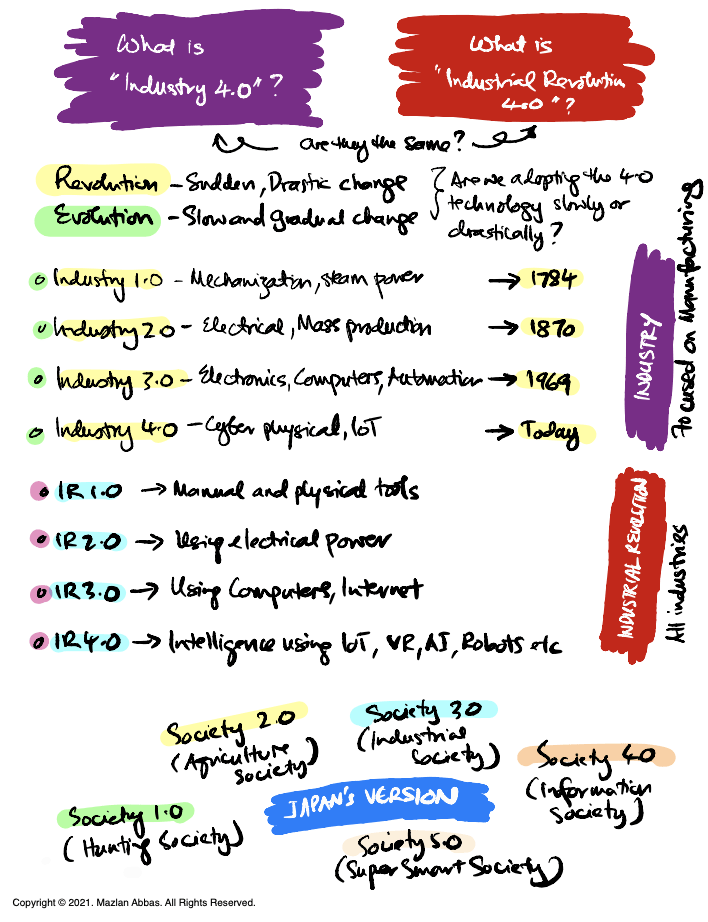
Today, we’ll explore two closely related but distinct concepts: Industry 4.0 and the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR 4.0).
These terms are often used interchangeably but have specific differences, as highlighted in the diagram. Let’s dive in step by step.
1. Revolution vs Evolution
The first thing we need to clarify is the difference between revolution and evolution:
- Revolution refers to sudden and drastic change. Think of it as a leap forward that quickly transforms industries and societies.
- Evolution, on the other hand, is slow and gradual progress. Changes happen incrementally over time.
Key question: Are we adopting Industry 4.0 technologies suddenly (revolution) or gradually (evolution)? This can vary depending on the industry and region.
2. What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 focuses on manufacturing and improving industrial processes through advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics. It is the fourth stage in the progression of industrial advancements:
Industry 1.0 (1784):
- Introduction of mechanisation and steam power.
- Example: Steam engines powering factories.
Industry 2.0 (1870):
- Electrical power enabled mass production.
- Example: Assembly lines in factories.
Industry 3.0 (1969):
- Use of computers, electronics, and automation.
- Example: Robots performing repetitive tasks on manufacturing floors.
Industry 4.0 (Today):
- Cyber-physical systems integrating IoT, AI, VR, and robotics.
- Example: Smart factories where machines communicate and operate autonomously.
3. What is Industrial Revolution 4.0 (IR 4.0)?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution goes beyond manufacturing. It’s about integrating these technologies across all industries and even societies. While Industry 4.0 focuses on production, IR 4.0 impacts healthcare, education, agriculture, and more.
A key question: Are we adopting these 4.0 technologies evenly across all sectors, or is there a focus on specific areas like manufacturing?
4. The Connection Between Industry 4.0 and IR 4.0
Think of Industry 4.0 as a subset of the broader IR 4.0. Industry 4.0 is about the transformation of manufacturing, whereas IR 4.0 encompasses societal changes.
Here’s an example:
- Industry 4.0: A factory using IoT sensors to monitor equipment health and reduce downtime.
- IR 4.0: IoT sensors used in agriculture to monitor soil moisture for precision farming.
5. Societal Progression Through Industrial Revolutions
The diagram also highlights how societies have evolved alongside industrial advancements:
- Society 1.0: Hunting society — Humans relied on nature and survival skills.
- Society 2.0: Agriculture society- farming practices transformed societies.
- Society 3.0: Industrial society — industries became the backbone of economies.
- Society 4.0: Information society – driven by computers and the internet.
- Society 5.0 (Japan’s Vision):
- A super-smart society where technology integrates seamlessly to improve quality of life.
- Focus on AI, robotics, and IoT to solve societal challenges.
6. Why is This Important?
Understanding these concepts helps us prepare for the future:
- For businesses: Knowing the difference between Industry 4.0 and IR 4.0 helps align strategies.
- For individuals: Skills like AI, IoT, and data analytics are becoming essential.
- For society: IR 4.0 encourages us to consider how technology can address global challenges like sustainability and healthcare.
Final Thoughts: Industry 4.0 is revolutionising manufacturing, while IR 4.0 is shaping the future of entire societies.
As we move forward, we aim to embrace these technologies for efficiency and to build a more intelligent, inclusive world.
[You can download the IoT Notes here]
