Examples of IoT Applications and Their Benefits
January 23rd, 2025 Posted by favoriotadmin BLOG 0 thoughts on “Examples of IoT Applications and Their Benefits”Today, let’s look at some real-world examples of IoT applications and their benefits.
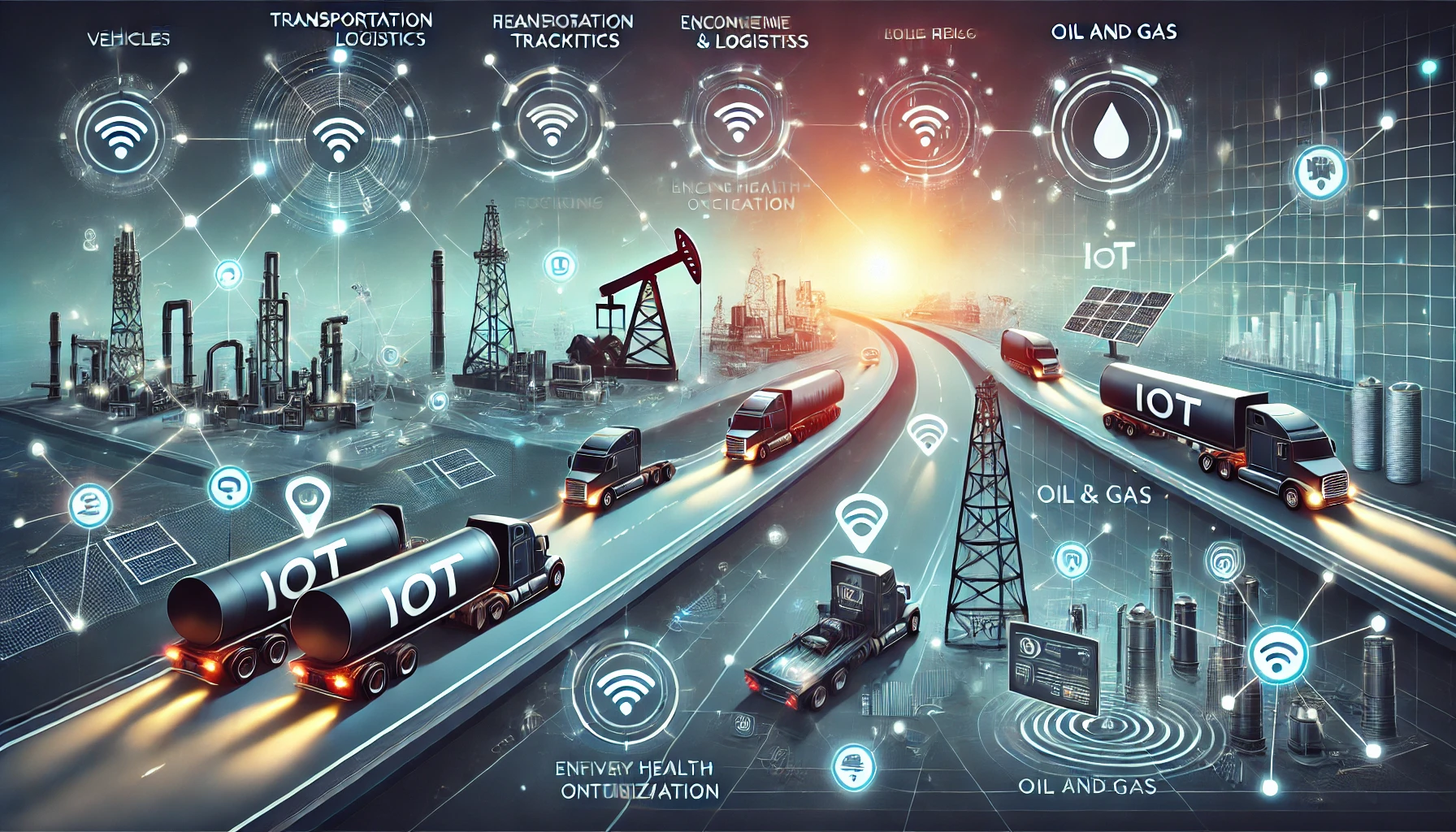
This diagram focuses on two industries—transportation and logistics and Oil and gas —to illustrate how IoT solutions can reduce costs and improve efficiency. Let’s examine each example in detail.

1. Transportation & Logistics
In this industry, IoT solutions are used to improve the management of vehicles and delivery systems.
IoT Solution:
- Sensors are installed in vehicles to provide real-time data on their state and performance.
- These sensors report on engine health, location, and delivery progress.
Benefits (Payback):
Cost Savings:
- Reduces truck operation and delivery costs by identifying and addressing maintenance issues early.
- Minimises fuel consumption by optimising delivery routes.
Improved Efficiency:
- Reduces delivery disruptions and delays.
- Ensures on-time deliveries and improves overall logistics system performance.
Example in Action: A logistics company uses IoT-enabled fleet management to track delivery vehicles and proactively schedule maintenance, avoiding breakdowns and saving costs.
2. Oil & Gas
The Oil & Gas industry faces unique challenges that IoT can address by enhancing safety and efficiency.
IoT Solution:
- Sensors are deployed throughout an oil rig to monitor critical components.
- These sensors detect potential issues and provide operators with real-time alerts.
Benefits (Payback):
Cost Savings:
- Increases safety by providing early and reliable warnings of potential equipment failures.
- Prevents costly shutdowns by identifying problems before they escalate.
Improved Efficiency:
- Real-time alerts enable quicker responses, reducing downtime and improving time-to-revenue.
- Enhances asset utilisation by ensuring equipment operates optimally (4x improvement).
- Complete data analysis allows for near real-time decision-making and operational adjustments.
Example in Action: An oil rig uses IoT sensors to monitor drill performance and prevent malfunctions, ensuring smoother operations and faster oil extraction.
Key Takeaways
IoT in Transportation & Logistics:
- Reduces costs and enhances delivery efficiency through real-time monitoring of vehicles.
IoT in Oil & Gas:
- Improves safety, reduces downtime, and maximises asset utilisation with real-time alerts and analysis.
Final Thought: IoT transforms industries by providing actionable data that saves money and improves efficiency. These examples show how IoT can adapt to specific industry needs and bring measurable benefits.
Discussion Question: Which other industries do you think can benefit from similar IoT solutions? Let’s brainstorm together!