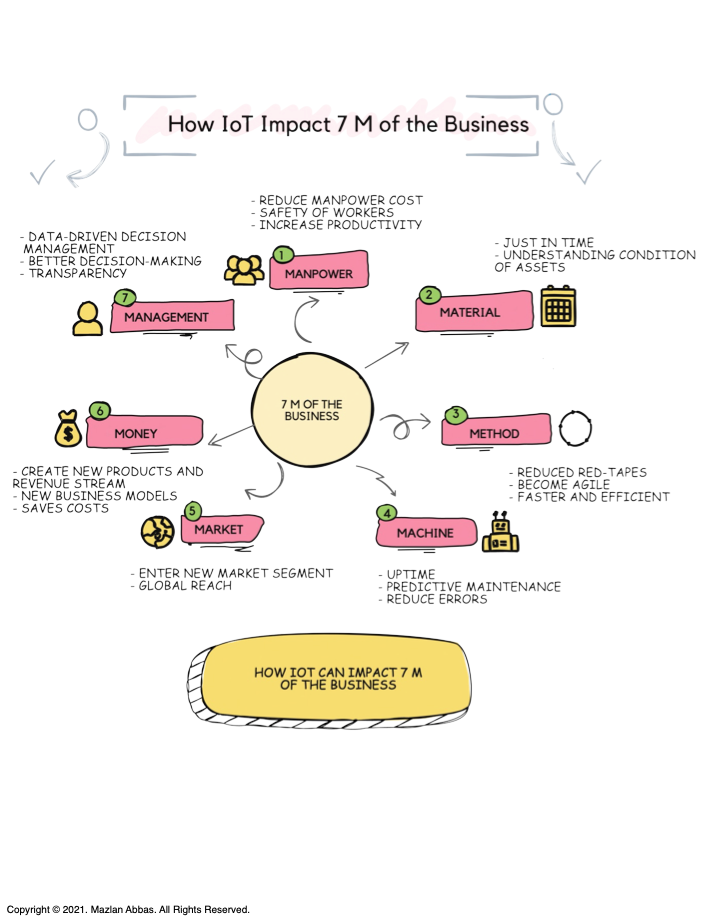
How IoT Impacts the 7 M’s of Business
January 2nd, 2025 Posted by favoriotadmin BLOG 0 thoughts on “How IoT Impacts the 7 M’s of Business”Today, we’ll explore how the Internet of Things (IoT) transforms the 7 M’s of business — key elements that drive an organisation’s operations and strategy.
These 7 M’s are Manpower, Material, Method, Machine, Market, Money, and Management. Let’s break down each one and see how IoT impacts them.
1. Manpower
IoT helps businesses optimise human resources by reducing costs, improving safety, and increasing productivity.
Impact of IoT:
- Cost Reduction: Automating repetitive tasks reduces the need for manual labour.
- Worker Safety: IoT devices, such as wearables, can monitor health and alert workers to potential hazards.
- Productivity: By enabling remote work and real-time communication, IoT allows employees to focus on high-value tasks.
Example: A construction company using wearables to monitor worker fatigue and ensure safety.
2. Material
IoT ensures better management of materials, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing waste.
Impact of IoT:
- Just-In-Time Delivery: Sensors track inventory levels and automatically reorder materials when needed.
- Asset Condition Monitoring: IoT devices monitor the condition of materials, ensuring quality and preventing spoilage.
Example: A warehouse using IoT sensors to track stock levels and ensure optimal storage conditions.
3. Method
IoT makes business processes more agile and efficient by simplifying methods.
Impact of IoT:
- Reduce Red Tape: Automating workflows eliminates unnecessary administrative steps.
- Agility: IoT enables businesses to respond quickly to changing conditions.
- Efficiency: Processes become faster and more streamlined with IoT integration.
Example: A manufacturing plant automating quality checks with IoT sensors to speed up production.
4. Machine
IoT maximises the performance of machines, ensuring reliability and reducing downtime.
Impact of IoT:
- Uptime: Predictive maintenance ensures machines are operational when needed.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors detect issues before they become critical, preventing failures.
- Error Reduction: Machines can self-correct or alert operators when errors occur.
Example: A factory using IoT-enabled machinery to monitor performance and schedule maintenance.
5. Market
IoT helps businesses expand into new markets and improve their customer reach.
Impact of IoT:
- New Market Segments: IoT enables innovative products and services, opening new revenue streams.
- Global Reach: Businesses can monitor and manage operations worldwide through IoT platforms.
Example: An IoT-enabled home security company entering international markets with smart security systems.
6. Money
IoT creates new revenue opportunities and reduces costs.
Impact of IoT:
- New Revenue Streams: IoT drives innovation, leading to new services and products.
- Cost Savings: Automating processes and improving efficiency reduces expenses.
Example: A logistics company saving fuel costs by using IoT to optimise delivery routes.
7. Management
IoT improves decision-making through data-driven insights.
- Impact of IoT:
- Data-Driven Decisions: Real-time data helps managers make informed choices.
- Transparency: IoT provides visibility into all areas of the business.
- Better Decision-Making: Analytics from IoT systems offer actionable insights.
Example: A retail chain using IoT to monitor sales trends and optimise inventory.
Key Takeaways
IoT has a transformative impact on the 7 M’s of business:
- Manpower: Reduces costs and improves safety.
- Material: Ensures quality and efficiency.
- Method: Simplifies workflows and increases agility.
- Machine: Enhances reliability and performance.
- Market: Expands opportunities globally.
- Money: Generates new revenue and reduces costs.
- Management: Improves decisions with real-time insights.
Discussion Question: Which of the 7 M’s most benefits from IoT in your industry? Let’s share ideas and examples!