MQTT vs HTTP Protocol: Part-2
February 5th, 2025 Posted by favoriotadmin BLOG, Internet of Things, IOT PLATFORM 0 thoughts on “MQTT vs HTTP Protocol: Part-2”Today, we’re diving deeper into comparing two commonly used communication protocols in IoT and the internet: MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) and HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol). Both protocols have distinct use cases; understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right one for IoT applications.

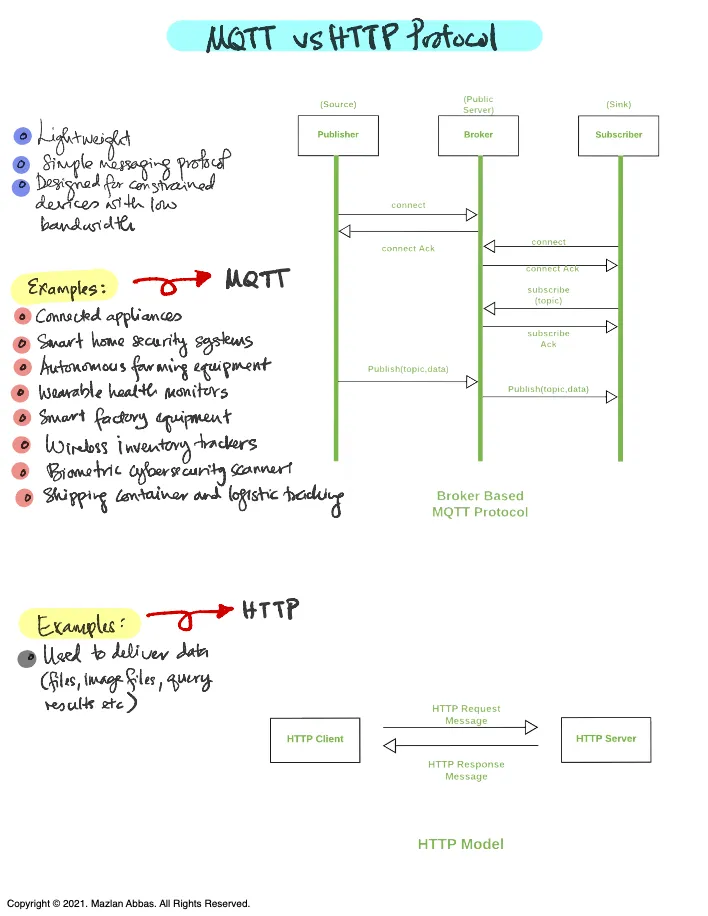
1. MQTT Protocol
MQTT is a lightweight, efficient protocol designed for low-bandwidth environments, making it ideal for IoT devices.
How MQTT Works
- Publisher-Subscriber Model: MQTT relies on a broker-based architecture.
- Publisher: Sends data (topics) to a central broker.
- Broker: Acts as the middleman that forwards the data to subscribers who have requested that topic.
- Subscriber: Receives the data they subscribed to via the broker.
Key Characteristics of MQTT
- Lightweight and low complexity.
- It is ideal for constrained devices with limited resources.
- Suited for real-time data delivery with minimal delays.
Examples of MQTT Applications
- Connected Appliances: Smart refrigerators and ovens sharing operational data.
- Smart Home Security Systems: Cameras and motion sensors communicate alerts in real-time.
- Autonomous Farming Equipment: Sensors monitoring soil and weather conditions.
- Wearable Health Monitors: Heart rate and activity trackers syncing data to a smartphone.
- Wireless Inventory Trackers: RFID and IoT tags tracking inventory in warehouses.
- Shipping and Logistics: Containers with IoT sensors send location and condition updates.
2. HTTP Protocol
HTTP is a robust and widely used protocol designed for document delivery over the Internet.
How HTTP Works
- Request-Response Model:
- HTTP Client: Sends a request to the server (e.g., to load a webpage or retrieve data).
- HTTP Server: Processes the request and sends back the response.
Key Characteristics of HTTP
- Designed for transferring web-based documents, such as HTML files, images, and query results.
- It works well for applications where low latency isn’t critical.
- It is more complex compared to MQTT, with higher bandwidth usage.
Examples of HTTP Applications
- Delivering large files, such as documents, images, and videos.
- Retrieving query results for web applications.
- Providing data for APIs in cloud-based services.
Comparing MQTT and HTTP
Let’s break down the main differences:
- Architecture: MQTT uses a broker for communication, while HTTP relies on a direct request-response model.
- Complexity: MQTT is lightweight and less complex, making it ideal for IoT devices. HTTP is more resource-intensive.
- Use Cases: MQTT is used for real-time, continuous communication in IoT systems. HTTP is better suited for traditional web applications and file transfers.
Choosing the Right Protocol
- Use MQTT when:
- You need real-time data transfer.
- Devices operate in low-bandwidth or resource-constrained environments.
- Applications involve frequent updates, like monitoring temperature or location.
- Use HTTP when:
- You need to deliver documents or large files.
- Data isn’t time-sensitive.
- The system supports higher bandwidth and can handle more complex communication.
Key Takeaway
Both protocols are valuable, but their application depends on the use case:
- MQTT is lightweight and efficient, designed for IoT systems needing real-time updates.
- HTTP is robust and versatile, ideal for traditional web applications.
Discussion Question: Based on this comparison, which protocol would you choose for a smart agriculture system, and why? Let’s discuss your thoughts!
