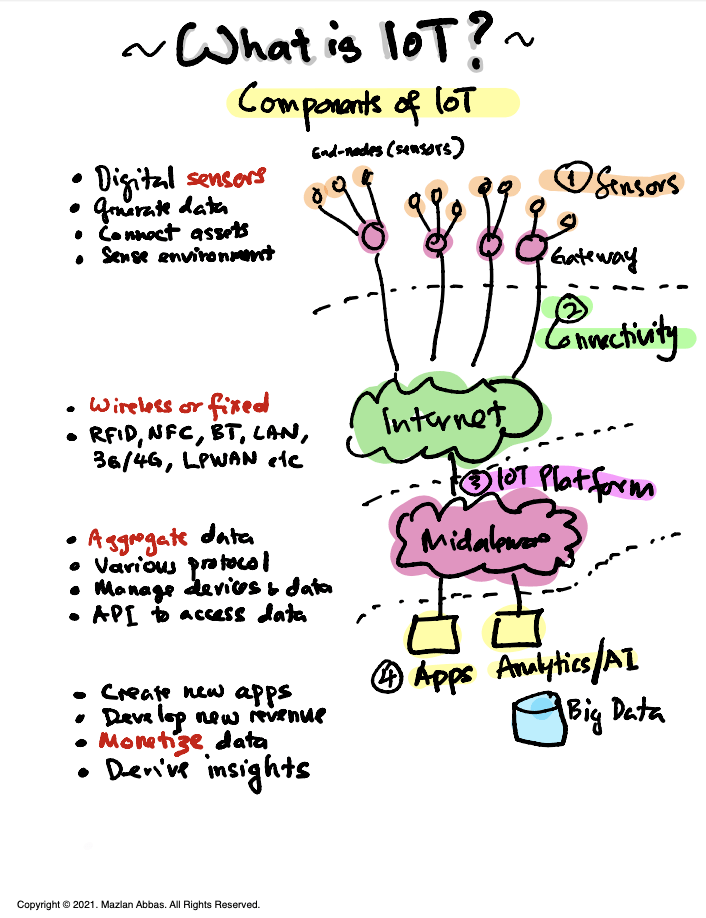
Let’s discuss an essential concept in IoT — its key components. The diagram breaks IoT into four main building blocks, which we’ll explore step by step.
1. Sensors: The Eyes and Ears of IoT
The first layer is the sensors. These devices are at the heart of IoT; their job is to sense the environment.
- They generate data by measuring things like temperature, humidity, or motion.
- Think of them as the “end-nodes” in IoT — they are where the process begins.
Examples include:
- A digital thermometer sensing room temperature.
- A motion detector in a security system.
Without sensors, IoT wouldn’t have any information to work with!
2. Connectivity: The Communication Bridge
Once sensors collect data, it needs to be transferred somewhere for processing. That’s where connectivity comes in.
- IoT uses different communication technologies:
- Wireless options like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LPWAN (LoRa or Sigfox).
- Fixed methods like Ethernet.
- Connectivity ensures the data travels from the sensors to the next stage over the internet or private networks.
Imagine this as a digital highway connecting the physical world to the virtual one.
3. IoT Platform and Middleware: The Brain
The third component is the IoT platform or middleware. This is where all the raw data comes together and is processed.
- It acts as a central hub to aggregate data from multiple sensors.
- Middleware handles:
- Device management.
- Data storage and formatting using standard protocols.
- Providing APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) so apps can access the data.
Think of this as the “brain” that processes everything and makes sense of the data.
4. Applications and Analytics: Deriving Insights
Finally, all the processed data is used in applications and analytics to deliver value. This is where IoT makes an impact.
Applications:
- Use the data to create useful solutions, like apps that track fitness or control smart homes.
- Analytics and AI:
- Analyse the data using Artificial Intelligence or Big Data techniques.
- Generate insights to help make decisions or automate processes.
For example:
- A smart farming app could use soil moisture data to trigger irrigation.
- An AI system could predict machine failure in a factory.
Bringing It All Together
So, to summarise:
- Sensors collect the data.
- Connectivity transmits the data.
- IoT Platform processes and stores the data.
- Applications and Analytics use the data to create actionable insights.
IoT is a powerful combination of hardware, communication, and software working together to solve real-world problems.
[Note: Based on the eBook – IoT Notes by Mazlan Abbas] <– FREE Download