What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
December 24th, 2024 Posted by favoriotadmin BLOG 0 thoughts on “What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?”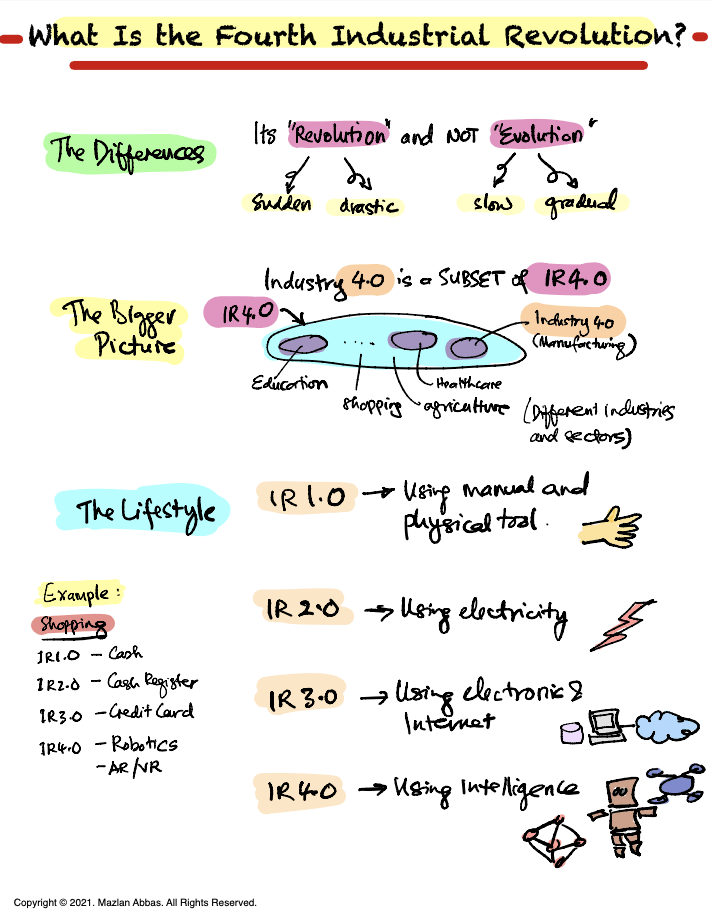
Today, we’ll explore the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR 4.0) and its significance. This diagram breaks it down into easy-to-understand sections, so let’s walk through it step by step.
1. The Differences Between Revolution and Evolution
Let’s first clarify why it’s called a revolution and not an evolution.
Revolution:
- Sudden and drastic changes that transform industries and societies.
- Think of it as a dramatic leap forward in technology and processes.
Evolution:
- Gradual and slow progress over time.
IR 4.0 is a revolution because it represents rapid and significant advancements in how we live and work.
2. The Bigger Picture: Industry 4.0 vs IR 4.0
It’s important to understand that Industry 4.0 is just a subset of IR 4.0.
- Industry 4.0 focuses on manufacturing and improving industrial processes using automation, IoT, and robotics.
- IR 4.0, however, encompasses much more:
- It impacts various sectors, such as education, healthcare, shopping, and agriculture.
- It’s a broad transformation, not limited to factories or industries.
3. The Lifestyle Through Industrial Revolutions
Let’s now look at how each industrial revolution shaped our lifestyle:
IR 1.0 — The Age of Manual Tools:
- People relied on physical and manual tools for work.
- Example: Ploughing fields with hand tools.
IR 2.0 — The Power of Electricity:
- Electricity revolutionised industries, enabling mass production.
- Example: Electric machines replaced manual labour.
IR 3.0 — The Digital Era:
- The rise of electronics and the internet connected the world.
- Example: Computers, email, and early e-commerce.
IR 4.0 — The Intelligence Revolution:
- We’re now using intelligence through AI, robotics, and advanced technologies.
- Example: Autonomous robots, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR).
4. Example: How Shopping Evolved
Let’s take shopping as an example of how each industrial revolution changed this activity:
- IR 1.0: People used cash for transactions.
- IR 2.0: The cash register was introduced, improving the checkout process.
- IR 3.0: Credit cards and online shopping emerged with the internet.
- IR 4.0: We see robotics and AR/VR enhancing the shopping experience, like virtual try-ons or automated warehouses.
Why is IR 4.0 Important?
IR 4.0 is transforming every aspect of our lives, from how we work and learn to how we interact with technology. It’s about leveraging intelligence to solve problems, improve efficiency, and create new possibilities.
[Note: You can download the full eBook — IoT Notes by Mazlan Abbas]